What Does Project 2025 Say About IVF?
April 15, 2025
How Much Does IVF Really Cost? Your Complete Guide to Understanding In Vitro Fertilization Expenses
April 15, 2025What Is FET in IVF? Your Ultimate Guide to Frozen Embryo Transfer

What Is FET in IVF? Your Ultimate Guide to Frozen Embryo Transfer
When you’re exploring the world of in vitro fertilization (IVF), you might stumble across the term “FET” and wonder what it means. FET stands for Frozen Embryo Transfer, a key part of many IVF journeys that’s growing in popularity. It’s a process where an embryo, previously created and frozen, gets thawed and placed into the uterus to hopefully grow into a healthy pregnancy. If you’re curious about how it works, why it’s done, or whether it’s right for you, you’re in the right place. This guide dives deep into everything you need to know about FET in IVF—think of it as your friendly roadmap to understanding this amazing option.
IVF can feel overwhelming, but FET offers a unique twist that’s worth exploring. It’s not just about fresh embryos anymore—freezing them gives you flexibility, better timing, and sometimes even higher success rates. Whether you’re new to fertility treatments or looking to expand your knowledge, this article will walk you through the details with a warm, approachable vibe. Let’s break it down step by step and uncover some fresh insights along the way.
Why FET Matters in IVF
Frozen Embryo Transfer has become a game-changer in the fertility world. Unlike the traditional IVF method where embryos are transferred fresh (right after they’re created), FET uses embryos that have been frozen and stored for later use. This shift isn’t just a small tweak—it’s opened up new possibilities for hopeful parents.
The beauty of FET lies in its flexibility. Maybe your body needs a break after the egg retrieval process, or perhaps your doctor wants to optimize your uterine lining before the transfer. Freezing embryos lets you hit pause and proceed when the timing’s just right. Plus, advancements in freezing technology—like vitrification, a super-fast freezing method—have made FET more reliable than ever. Studies show that vitrification has boosted embryo survival rates to over 95%, a huge leap from older techniques.
But why is FET such a big deal? For one, it can increase your chances of success. Research from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) suggests that FET often leads to higher pregnancy rates compared to fresh transfers in certain cases. Why? Because it gives your body time to recover from the hormonal rollercoaster of IVF stimulation, letting your uterus prep for the best possible welcome.
How Does Frozen Embryo Transfer Work?
So, how does FET actually happen? It’s a multi-step process that’s both science and a little bit of magic. Here’s a breakdown of what goes down:
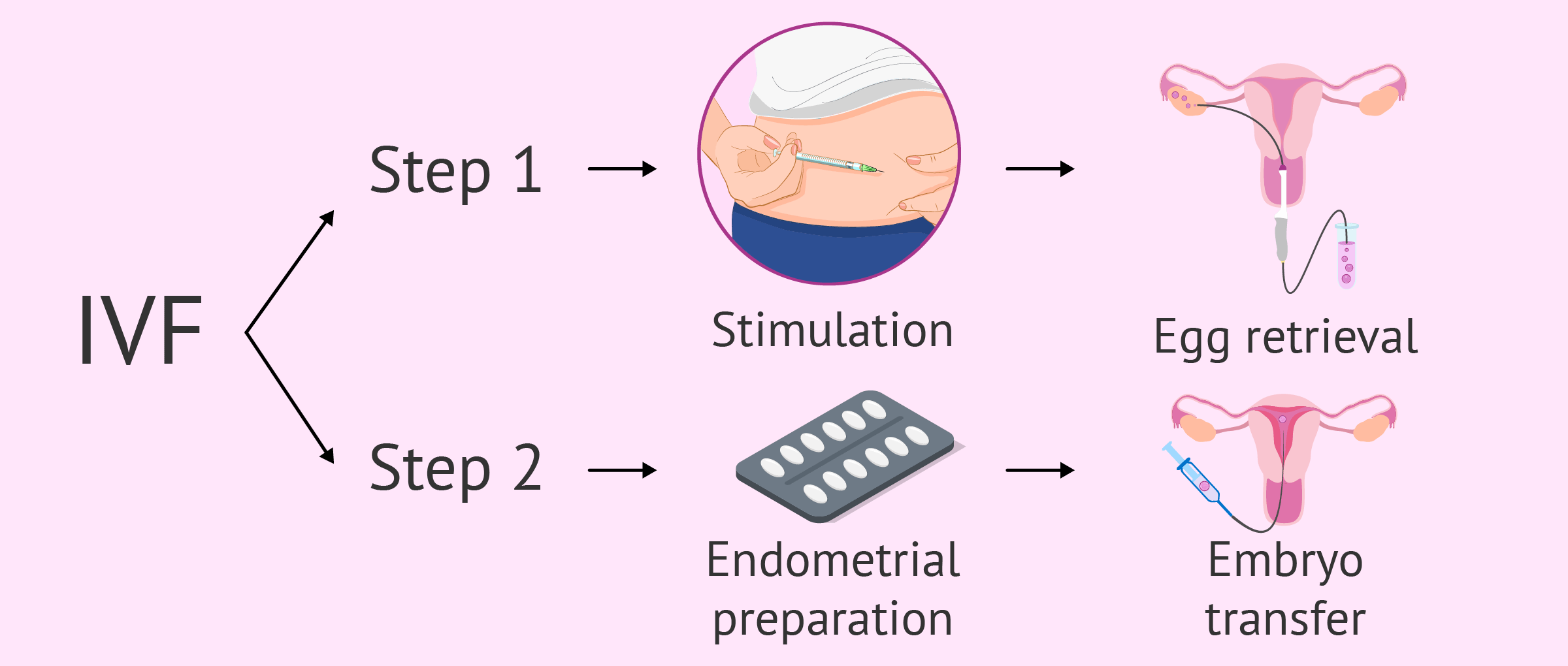
Step 1: Creating and Freezing Embryos
First, you go through the standard IVF process—your eggs are retrieved, fertilized with sperm in a lab, and turned into embryos. Instead of transferring them right away, the healthiest ones are frozen using vitrification. This flash-freezing technique protects the embryos by turning them into a glass-like state, avoiding ice crystals that could damage them.
Step 2: Preparing Your Body
When you’re ready for the transfer (which could be days, months, or even years later), your doctor will prep your uterus. This might involve a “natural cycle” where they track your ovulation, or a “medicated cycle” where hormones like estrogen and progesterone get your lining in tip-top shape. The goal? A cozy, thick uterine lining—usually around 7-10 millimeters—ready to host an embryo.
Step 3: Thawing and Transferring
On transfer day, the lab thaws your chosen embryo (don’t worry, survival rates are sky-high with modern tech). Using a thin catheter, your doctor gently places it into your uterus. It’s a quick procedure—think 10-15 minutes—and you’ll likely be awake, maybe even watching it on an ultrasound screen. Afterward, you rest briefly and head home to wait.
Step 4: The Two-Week Wait
Now comes the nail-biting part: waiting about 10-14 days for a pregnancy test. Your doctor might check your hormone levels or have you take a home test. It’s a mix of hope and patience, but knowing the process can make it feel less mysterious.

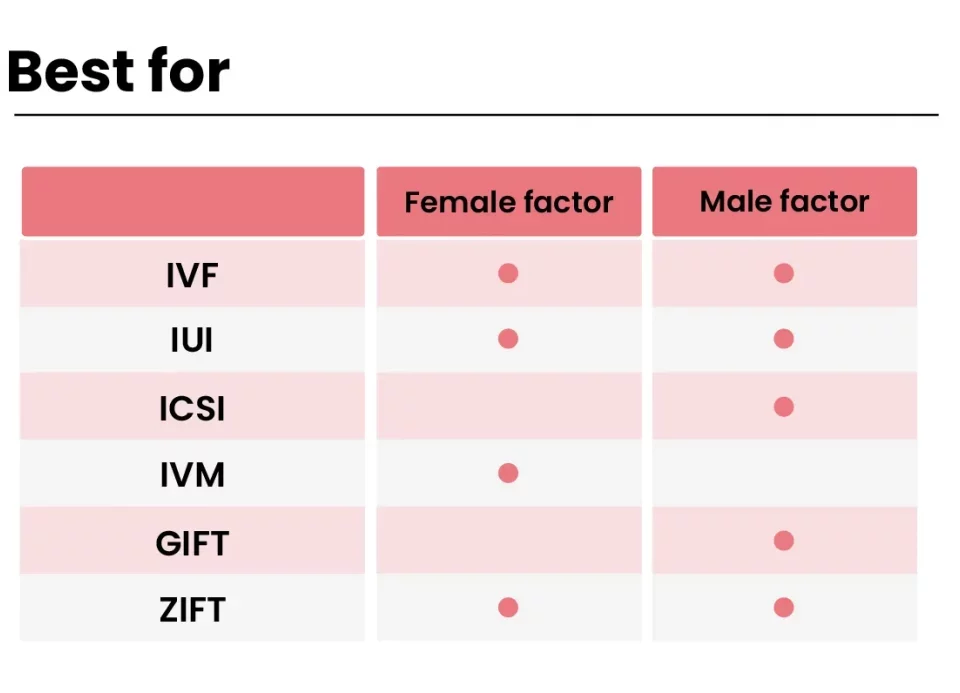
Fresh vs. Frozen: What’s the Difference?
You might be wondering, “Why freeze embryos at all? Why not just use them fresh?” Great question! Both fresh and frozen transfers have their perks, but they serve different needs. Let’s compare them:
| Aspect | Fresh Transfer | Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Happens right after egg retrieval | Can happen anytime—days or years later |
| Body Recovery | No break from hormones | Gives your body a rest before transfer |
| Success Rates | Good, but can vary | Often higher due to better timing |
| Flexibility | Less—tied to your cycle | More—plan it when it suits you |
| Embryo Quality | Used fresh, no thawing risk | Top-notch freezing preserves quality |
A 2023 study in Fertility and Sterility found that FET success rates can hit 60-70% per transfer for women under 35, compared to 50-60% for fresh transfers. The difference? FET lets doctors sync the transfer with your body’s natural rhythm, avoiding overstimulation from egg retrieval meds.
Who Should Consider FET?
FET isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, but it’s a fantastic option for many. Here are some folks who might benefit:
- People with Extra Embryos: If your IVF cycle produces more embryos than you need, freezing them lets you try again later without starting from scratch.
- Those Needing a Break: Egg retrieval can be tough on your body. FET gives you time to recover physically and emotionally.
- High-Risk Situations: If you’re at risk for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a rare but serious IVF side effect, FET delays the transfer until you’re safe.
- Genetic Testing Fans: Want to screen embryos for chromosomal issues? Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) takes time, so freezing is a must.
- Lifestyle Planners: Maybe you’re not ready for pregnancy now but want kids later—FET lets you store embryos for the future.
Real talk: I spoke to a friend who chose FET after her first fresh transfer didn’t work. She said the break between cycles helped her feel less stressed, and her second FET brought her a healthy baby boy. It’s not just science—it’s about what feels right for you.
The Science Behind FET Success
Let’s geek out for a minute. Why does FET often outperform fresh transfers? It’s all about biology and timing. During a fresh IVF cycle, your body’s pumped with hormones to grow eggs. That can throw your uterine lining off-balance—sometimes it’s too “revved up” to catch an embryo. FET flips the script by letting your hormones settle, creating a calmer, more natural environment.
A 2024 study from the University of California found that FET pregnancies had a 10% lower miscarriage rate than fresh ones. Researchers think it’s because the thawed embryos—already survivors of freezing—might be tougher. Plus, doctors can fine-tune your lining with meds or wait for your natural cycle, boosting the odds of implantation.
Here’s a fun fact: embryos can stay frozen indefinitely without losing quality. There’s even a case of a baby born in 2021 from an embryo frozen for 27 years! That’s a testament to how far freezing tech has come.
What to Expect During Your FET Journey
Ready to picture yourself in the FET process? Here’s what it might look like, from prep to post-transfer:
Before the Transfer
- Consultation: You’ll chat with your doctor about timing, meds, and which embryo to use.
- Monitoring: Expect a few ultrasounds and blood tests to check your lining and hormones.
- Meds (if needed): Pills, patches, or shots—estrogen and progesterone are your new besties.
Transfer Day
- Quick and Easy: You’ll lie back, the catheter does its thing, and you’re done in minutes.
- Comfort Tips: Wear cozy socks, bring a playlist, and relax—stress won’t help!
After the Transfer
- Rest, but Don’t Overdo It: Take it easy for a day, but you don’t need bed rest—studies show normal activity is fine.
- Symptoms to Watch: Light spotting or cramping is normal; heavy bleeding or pain isn’t—call your doc if that happens.
- Mindset: Keep busy with light distractions—binge a show, knit, or walk your dog.
Busting FET Myths
There’s a lot of chatter out there about FET, and not all of it’s true. Let’s clear up some common misconceptions:
- Myth: Frozen embryos aren’t as good as fresh ones.
Truth: Nope! Modern freezing keeps embryos just as viable—sometimes even better—than fresh ones. - Myth: FET is riskier for babies.
Truth: Research, like a 2022 study in Human Reproduction, shows FET babies are as healthy as fresh-transfer ones, with no extra risks. - Myth: It’s super expensive.
Truth: While costs vary (around $3,000-$5,000 per cycle in the U.S.), FET is often cheaper than a full fresh IVF round since you skip egg retrieval.
Interactive Quiz: Is FET Right for You?
Curious if FET fits your journey? Take this quick quiz! Jot down your answers and see where you land.
- Do you have extra embryos from a past IVF cycle?
A) Yes
B) No - Are you okay with waiting a bit before pregnancy?
A) Totally fine
B) I’d rather not - Does the idea of genetic testing interest you?
A) Yes, I’d love that
B) Not really - Want to give your body a break after egg retrieval?
A) Definitely
B) I’m good to go now
Mostly A’s? FET could be your vibe—talk to your doctor!
Mostly B’s? A fresh transfer might suit you better, but FET’s still worth a chat.
Three Things You Haven’t Heard About FET
Most articles cover the basics, but here are three under-the-radar insights that add depth to your FET knowledge:
1. FET Can Reduce Stress Hormones
Unlike fresh cycles, FET skips the intense stimulation phase right before transfer. A 2023 study in Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics found that women doing FET had lower cortisol (stress hormone) levels during the process. Less stress could mean a happier uterus—and maybe a better shot at success.
2. Frozen Embryos Might Be Genetic Superstars
Ever wonder why some embryos thrive after thawing? Scientists think the freezing process acts like a natural filter. Only the strongest embryos survive vitrification, meaning you’re transferring the cream of the crop. It’s like nature’s own quality control!
3. FET’s Role in Single Embryo Transfers
More clinics are pushing single embryo transfers (SET) to avoid twins and triplets, which carry higher risks. FET makes SET easier because you can freeze extras and transfer one at a time. A 2024 report from the CDC showed SET with FET cut multiple births by 15% compared to fresh cycles.

Tips for a Successful FET
Want to stack the deck in your favor? Here are some practical, research-backed tips:
✔️ Eat for Your Lining: Load up on foods rich in vitamin E (nuts, spinach) and omega-3s (salmon, chia seeds)—they support a thick, healthy uterine lining.
✔️ Stay Warm: Some studies suggest keeping your feet warm boosts pelvic blood flow. Cozy socks, anyone?
✔️ Hydrate: Drinking water helps your body handle meds and keeps things flowing smoothly.
❌ Don’t Overstress: Skip the “I must stay still” mindset—gentle movement is better than obsessing.
❌ Avoid Crash Diets: Extreme weight loss can mess with hormones—aim for balance instead.
One unique tip? Try acupuncture. A 2022 meta-analysis in Reproductive BioMedicine Online found it might bump up FET success rates by 10-15% when done around transfer day. It’s not for everyone, but it’s a low-risk option to consider.
Real Stories: FET in Action
Sometimes, hearing from others makes it click. Meet Sarah, a 34-year-old teacher from Oregon. After two failed fresh transfers, she felt defeated. Her doctor suggested FET, explaining her body needed a reset. Six months later, with a medicated FET cycle, Sarah got her positive test. “It was like my body finally said yes,” she told me over coffee. Her daughter, Emma, just turned two.
Then there’s Mark and Lisa, a couple who froze embryos before Lisa’s cancer treatment. Years later, post-recovery, their FET brought twins. “Freezing gave us hope when everything else felt uncertain,” Mark shared. These stories show FET’s power—it’s not just science; it’s personal.
The Cost of FET: What to Budget
Money’s a biggie, right? FET costs less than a full IVF cycle, but it’s still an investment. Here’s a snapshot:
- Base Cost: $3,000-$5,000 per transfer (includes monitoring and procedure).
- Meds: $500-$1,500, depending on your protocol.
- Storage: $300-$600 per year for frozen embryos.
- Extras: Add $1,000-$2,000 if you’re doing genetic testing.
Pro tip: Check your insurance—some plans cover FET meds or storage now, thanks to growing fertility awareness. Also, clinics often offer payment plans, so don’t be shy about asking.
FET and the Future: What’s Next?
FET’s not standing still—new research is pushing boundaries. Scientists are exploring “artificial wombs” to grow embryos longer before freezing, potentially upping quality. Another hot topic? Using AI to pick the best embryos for thawing. A 2024 trial in Europe saw AI boost FET success by 8% by analyzing embryo images.
For you, this means FET could get even smarter and more tailored. Imagine a future where your doctor uses tech to predict your perfect transfer day with pinpoint accuracy. It’s not sci-fi—it’s coming.
Your FET Checklist
Before you dive in, here’s a handy checklist to keep you on track:
✔️ Talk to your doctor about FET pros and cons.
✔️ Ask about natural vs. medicated cycles—which fits you?
✔️ Check your embryo quality and count.
✔️ Plan your timeline—when’s your ideal transfer window?
✔️ Budget for costs and explore financial help.
Poll: What’s Your FET Curiosity?
Let’s get interactive! Vote below and see what others think:
What’s your biggest FET question?
A) How do I boost my success odds?
B) What’s the thawing process like?
C) How long can embryos stay frozen?
D) Other (share in your mind—I’d love to know!).
Results update weekly—check back to see where you fit!