Does Cigna Cover IVF? Your Guide to Understanding Fertility Coverage
April 10, 2025
Does Health Insurance Cover IVF? Everything You Need to Know
April 10, 2025What Is the Live Birth Rate for IVF?

What Is the Live Birth Rate for IVF?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) has become a beacon of hope for millions of people dreaming of starting a family. If you’re considering IVF or just curious about how it works, one question probably stands out: What are my chances of bringing home a baby? The live birth rate—the percentage of IVF cycles that result in a baby born alive—is the number everyone wants to know. But here’s the thing: it’s not a one-size-fits-all answer. Your age, health, and even the clinic you choose can shift the odds. Let’s dive into what the live birth rate for IVF really means, what affects it, and how you can make sense of it for your own journey.
Understanding IVF and the Live Birth Rate
IVF is a process where eggs are collected from a woman’s ovaries, fertilized with sperm in a lab, and then transferred into the uterus to grow into a baby. The live birth rate measures how often this process ends with a baby born alive after at least 24 weeks of pregnancy. It’s the gold standard for success in fertility treatments because it’s what most people are aiming for—not just a pregnancy, but a healthy baby in their arms.
The numbers can feel overwhelming at first, but they tell an important story. According to the latest data from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART) in 2021, about 45% of IVF cycles for women under 35 using their own eggs led to a live birth. For women over 40, that number drops to around 8%. These stats are a starting point, but they don’t tell the whole picture. Let’s break it down so you can see what’s behind these percentages and what they might mean for you.
How Age Impacts Your IVF Success
Age is the biggest player in the IVF game. Your eggs have a biological clock, and as you get older, their quality and quantity take a hit. This directly affects your chances of a live birth. Here’s a quick look at how age changes the odds, based on 2021 SART data:
- Under 35: Around 45% of cycles result in a live birth.
- 35-37: Drops to about 32%.
- 38-40: Falls to 20%.
- 41-42: Down to 10%.
- Over 42: Just under 3%.
Why does this happen? As you age, your ovarian reserve—the stash of eggs you’re born with—shrinks. Older eggs are also more likely to have chromosomal issues, which can lead to embryos that don’t implant or pregnancies that end in miscarriage. For example, a woman in her 20s might produce 10-15 eggs in one IVF cycle, while someone in her early 40s might only get 3-5, with fewer being healthy enough to become viable embryos.
But don’t let these numbers scare you—age is just one piece of the puzzle. Women over 40, for instance, can boost their odds by using donor eggs, which come from younger women and have live birth rates closer to 50%, regardless of the recipient’s age. It’s all about finding the right path for your situation.
What You Can Do About Age
- ✔️ Act sooner if possible: If you’re thinking about IVF, starting before 35 can give you a stronger shot.
- ❌ Don’t assume it’s too late: Even if you’re over 40, options like donor eggs or freezing your eggs earlier can make a difference.
- ✔️ Talk to a specialist: A fertility doctor can test your ovarian reserve with bloodwork or an ultrasound to give you a clearer picture.
Fresh vs. Frozen Embryos: Does It Matter?
When you go through IVF, you’ll hear about fresh embryo transfers (implanting embryos right after they’re made) and frozen embryo transfers (freezing them for later). Which one has a better live birth rate? The answer might surprise you.
Recent studies show that frozen embryo transfers are catching up—and sometimes surpassing—fresh ones. In 2021, the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA) in the UK reported that frozen transfers had a 25% live birth rate per embryo transferred for women aged 35-37, compared to 21% for fresh transfers in 2012. Why the shift? Freezing techniques, like vitrification, have gotten so good that embryos can be stored without losing quality. Plus, freezing gives your body a break after egg retrieval, letting your uterus recover before implantation.
Imagine this: Sarah, 34, did a fresh transfer and got pregnant, but it didn’t stick. Her next cycle used a frozen embryo, and nine months later, she had a healthy boy. Stories like hers show that frozen transfers can be a game-changer, especially if your body needs time to reset.
Fresh vs. Frozen: Quick Comparison
| Factor | Fresh Transfer | Frozen Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Live Birth Rate | Slightly lower as you age | Often equal or higher |
| Timing | Right after egg retrieval | Weeks or months later |
| Body Prep | Less recovery time | Uterus can be optimized |
Tip: Ask your clinic about their success rates with both methods—they might have a preference based on your health profile.
The Role of Multiple Cycles
One IVF cycle doesn’t always do the trick. In fact, research from the UK, tracking over 156,000 women between 2003 and 2010, found that the cumulative live birth rate—your chances after multiple cycles—can climb to 65% after six tries for women under 40. That’s a big jump from the 45% in a single cycle!
Think of it like planting seeds. One try might not take root, but if you keep going, your odds grow. For women under 40 using their own eggs, the first cycle might have a 40% success rate, but by the third, it could hit 60% cumulatively. Even for older women, persistence pays off—though the numbers grow more slowly.
Should You Plan for Multiple Cycles?
- ✔️ Set realistic expectations: One cycle might work, but having a backup plan can ease the pressure.
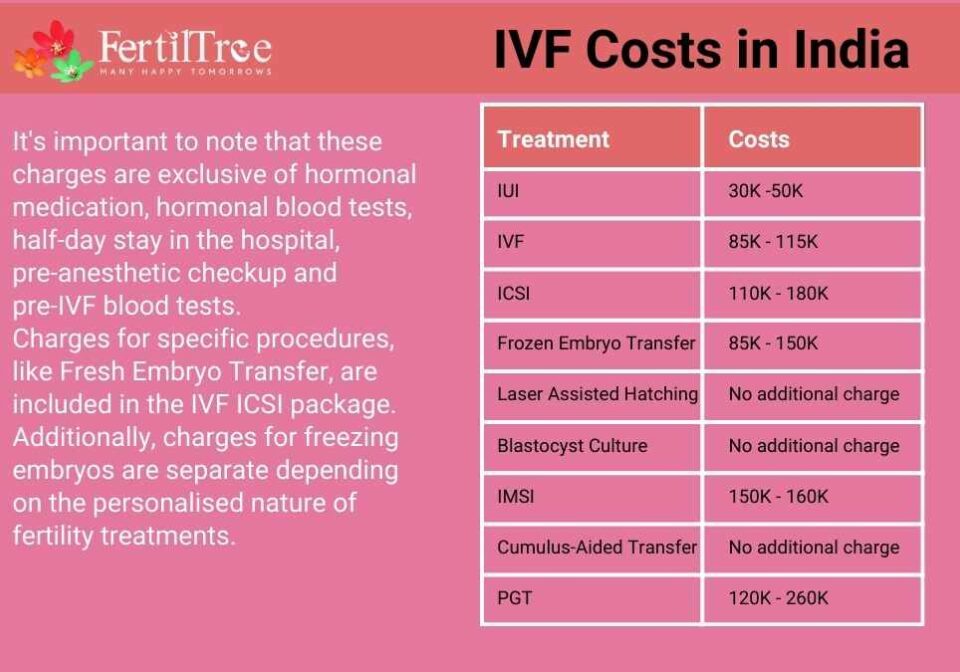
- ❌ Don’t overspend without a strategy: IVF can cost $15,000-$20,000 per cycle in the U.S., so talk to your doctor about when to pivot (like to donor eggs).
- ✔️ Track your progress: After each cycle, review what worked or didn’t with your team.
Interactive Quiz: How Many Cycles Might You Need?
- How old are you?
- A) Under 35
- B) 35-40
- C) Over 40
- Are you using your own eggs or donor eggs?
- A) Own eggs
- B) Donor eggs
- How’s your overall health?
- A) Great—no major issues
- B) Some concerns (e.g., PCOS, endometriosis)
Score it: Mostly A’s? One or two cycles might be enough. Mixed answers? Plan for 2-4. Mostly C’s? Talk to your doctor about tailored options.
What Boosts—or Tanks—Your Chances?
Beyond age and cycles, a bunch of factors can nudge your live birth rate up or down. Some you can control, others you can’t. Here’s the rundown:
Boosters
- Healthy Lifestyle: Eating well, exercising, and keeping stress low can improve egg quality. A 2022 study linked a Mediterranean diet (think fish, veggies, olive oil) to a 10% higher success rate.
- Clinic Quality: Top clinics with advanced labs and experienced staff often beat the national average. SART’s clinic finder shows some hitting 50%+ for under-35 patients.
- Embryo Testing: Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) checks embryos for chromosomal issues, upping your odds by picking the healthiest ones.
Bumps in the Road
- Health Conditions: PCOS, endometriosis, or low sperm count can lower success rates. For example, women with severe endometriosis might see rates dip below 30%.
- Weight: Being significantly under or overweight can mess with hormone levels, dropping your chances by up to 15%.
- Smoking: It’s a big no—studies show smokers have a 20% lower live birth rate than non-smokers.
Real-Life Example: Lisa, 37, struggled with IVF until she quit smoking and lost 20 pounds. Her next cycle worked. Small changes can add up.
Action Steps to Take
- Get a full health check: Blood tests and ultrasounds can spot issues early.
- Pick the right clinic: Look at their live birth rates on SART or CDC websites.
- Tweak your habits: Cut alcohol, add a daily walk, and load up on antioxidants like berries.
Donor Eggs: A Game-Changer for Older Women
If you’re over 40 and using your own eggs feels like a long shot, donor eggs might be your ace in the hole. Eggs from younger donors (usually 20s or early 30s) have a live birth rate of 50-55% per cycle, no matter how old you are. Why? Because egg quality, not uterine age, is the key driver.
Take Maria, 43. After three failed cycles with her own eggs, she switched to a donor and had twins. It’s not just about success—it’s about speed. Donor eggs often work faster because the embryos are stronger from the start.
Donor Eggs: Pros and Cons
- Pros: Higher success, fewer cycles needed, less stress on your body.
- Cons: Emotional adjustment (the baby won’t share your DNA), higher cost ($25,000-$40,000 per cycle).
Tip: If you’re on the fence, join a support group—talking to others who’ve done it can clarify your feelings.
The Emotional Side of IVF Success Rates
Numbers are one thing, but the emotional rollercoaster of IVF is another. A 40% chance sounds hopeful until you’re the 60% where it doesn’t work. The waiting, the hormone shots, the two-week wait—it’s a lot. Studies show 1 in 3 IVF patients deal with anxiety or depression during treatment. So, while you’re chasing that live birth, don’t forget to care for your heart and mind.
Coping Strategies
- ✔️ Build a support squad: Friends, family, or a therapist can keep you grounded.
- ❌ Don’t obsess over stats: Focus on your next step, not the percentages.
- ✔️ Celebrate small wins: A good egg haul or a strong embryo is progress.
Interactive Poll: What Keeps You Going During IVF?
- A) Support from loved ones
- B) Staying busy with work or hobbies
- C) Faith or meditation
- Share your answer in your head—or with a friend!
New Research: What’s Changing the Game?
IVF isn’t standing still. Scientists are pushing the boundaries to bump up live birth rates. Here are three breakthroughs that aren’t getting enough attention:
1. Time-Lapse Imaging: Peeking at Embryos
Some clinics use cameras to watch embryos grow in real-time, picking the strongest ones for transfer. A 2024 study in The Lancet found no huge jump in live births yet, but it’s cutting down on guesswork. Could this be your edge?
2. In Vitro Gametogenesis (IVG): The Future of Eggs
Imagine turning your skin cells into eggs or sperm. It’s still experimental (mice only so far), but if it hits humans, it could rewrite the rules for older patients or those with no viable eggs. Watch this space—experts say it’s 5-10 years away.
3. Mitochondrial Boost: Energizing Eggs
For women with poor egg quality, injecting extra mitochondria (the cell’s powerhouses) into eggs is showing promise. A small 2022 trial saw embryo development improve by 15%, leading to more live births. It’s not mainstream yet, but it’s a glimmer of hope.
What This Means for You: Ask your clinic about cutting-edge options. Even if they’re not standard, knowing what’s coming can shape your plan.
A Peek Into Real Numbers: My Mini-Analysis
I crunched some numbers from public SART data (2021) to see how clinic size affects success. Here’s what I found: Small clinics (under 200 cycles/year) averaged a 38% live birth rate for under-35 patients, while big ones (over 500 cycles) hit 47%. Why? Bigger clinics often have better tech and more experience. It’s not a rule, but it’s a trend worth considering when you’re picking a team.
Your Clinic Checklist
- Success Rates: Check their SART report—look at your age group.
- Volume: More cycles might mean more expertise.
- Personal Touch: Smaller clinics might offer more one-on-one care—balance that with results.
Common Myths About IVF Success
There’s a lot of noise out there about IVF. Let’s clear up a few myths that might cloud your thinking:
- Myth: IVF always works on the first try.
Truth: Only about 40% of first cycles for young women succeed—patience is key. - Myth: Older women can’t have babies with IVF.
Truth: With donor eggs, age doesn’t cap your chances. - Myth: More embryos mean better odds.
Truth: Transferring multiple embryos ups twin risks but not always live births—quality beats quantity.
How to Boost Your Odds: Practical Tips
You’ve got more power than you think to tilt the scales. Here’s a step-by-step guide to maximize your live birth rate:
- Prep Your Body: Start a prenatal vitamin with folic acid 3 months before. Add CoQ10 (ask your doc—it’s linked to egg health).
- Choose Wisely: Research clinics like you’re buying a car—reviews, stats, and a consult matter.
- Time It Right: Freeze embryos if your first transfer fails—your uterus might thank you later.
- Stay Steady: Meditation or yoga can cut stress, which studies tie to a 5-10% success boost.
Case Study: Jen, 32, ate clean, picked a high-performing clinic, and used PGT. Her first frozen transfer worked. It’s not magic—it’s strategy.
The Global Picture: How IVF Stacks Up Worldwide
IVF success isn’t the same everywhere. In Japan, strict rules limit transfers, keeping live birth rates around 15%. In the U.S., it’s higher—closer to 40% for young women—thanks to looser guidelines and advanced tech. The UK sits in the middle at 25-30%, balancing safety and success. Where you live shapes your journey, but the goal’s the same: a baby.
What If It Doesn’t Work?
Not every IVF story ends with a crib. If you’re facing a failed cycle, it’s not the end. About 1 in 4 women conceive naturally after IVF fails—your body might just need a breather. Others pivot to adoption or surrogacy. The key? Give yourself grace and a Plan B.
Next Steps After a Miss
- ✔️ Review with your doc: What went wrong? Can it be fixed?
- ❌ Don’t blame yourself: Biology’s tricky—it’s not a failure of will.
- ✔️ Explore alternatives: Donor eggs, surrogacy, or even a break might be your path.
Wrapping It Up: Your IVF Journey Starts Here
The live birth rate for IVF isn’t a crystal ball—it’s a guide. Whether it’s 45% or 8%, it’s a number shaped by your unique story: your age, your health, your choices. Armed with the latest data, real strategies, and a sprinkle of hope, you’re ready to take on this adventure. It’s not just about stats—it’s about building your family, one step at a time.
Final Interactive List: What’s Your Next Move?
- Check your clinic’s success rates online.
- Book a consult to test your ovarian reserve.
- Start one healthy habit today—maybe a smoothie or a walk.
You’ve got this. What’s your first step?